Exemples de trading sur forex
Contactez-nous au +41 (0) 58 810 77 43 pour toute question concernant l'ouverture d'un compte.
Become the first to know about the newest forex bonus from reliable brokers (forex and binary options) all over the world like free bonuses, forex brokers reviews, forex signals, after registration bonus, no deposit forex bonuses, demo contests, binary options bonus, and many other profitable advices, checked out and posted every day by our experienced columnists from forex and stock markets. Meet the #1 largest forex bonuses place of this year! Only all forex bonuses!
Contactez-nous au +41 (0) 58 810 77 43 pour toute question concernant l'ouverture d'un compte.
If yes, then you might be living in the dark due to insufficient knowledge regarding the no deposit bonus.
Getting ready to start your trading without committing an investment. No deposit bonus for newbies to try out services to start earning profit without risking any of their funds.
- you can place banner ads on your website. To download the binance affiliate design kit for ads, click here .
The following items are often seen in the control account questions. As these times are closely related to the "sales and trade receivables", students often confuse and record them in the S L control account. But these items should not be recorded in the control accounts. Lets check these items below. Total of trade receivable' balances at the end of the current accounting period.

Sales ledger control account is a summary account which checks the arithmetical accuracy of the sales ledger. It enables us to see at a glance whether the general ledger balance for the sales ledger agrees with the total of all the individual trade receivable accounts held within the sales ledger.
Sales ledger control account typically looks like a "T-account" or a replica of an individual trade receivable ( debtor) account, but instead of containing transactions related to one trade receivable (debtor) it contains transactions related to all the trade receivables (all the debtors) in the business. As this control account contains the summarized information of all the trade receivables accounts in the sales ledger, it is also called as "total trade receivables account"("total debtors account").
Check out the format of this control account below and try to perceive the similarities with individual trade receivable account (debtors account).
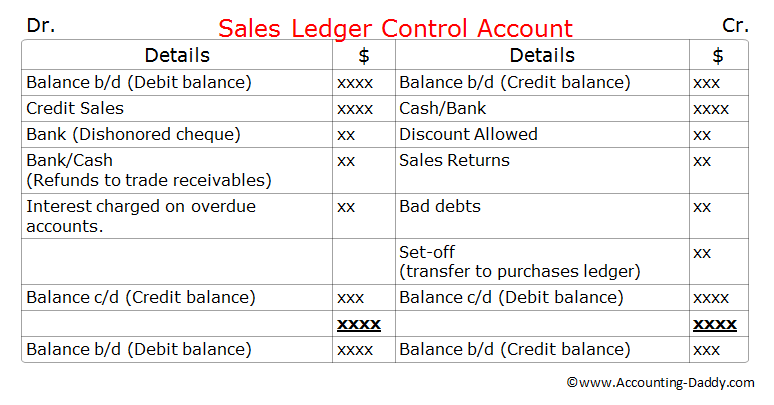
Sales ledger control account is generally prepared at the end of the financial year or "whenever" it is required to check the arithmetical accuracy of the individual trade receivable accounts.
As we discussed earlier, this control account is prepared as an independent check on the arithmetical accuracy of the sales ledger (debtors ledger). So, we should not obtain the information required to prepare this control account from the sales ledger (debtors ledger), instead all the information required should be obtained from books of original entry or prime entry.
Once the control account is prepared using the above format with the information obtained from various books of prime entry/original entry, the total of balances on the individual trade receivable accounts in the sales ledger should match with the closing balances on the sales ledger control account.
If the closing balances of sales ledger control and the total of balances on the individual trade receivable accounts in the sales ledger agrees, we can presume that there are no errors or fraud occurred in the sales ledger. If the balances differ, it indicate that there are errors in the individual trade receivables accounts in the sales ledger or in the control account. So to locate these errors, accountants need to check each and every trade receivables account in the sales ledger carefully until the error is found or the fraud is detected.
The following table provides the details of source of information for the sales ledger control account items.
Source of information
Opening trade receivables (opening debtors)
Total of trade receivable' balances at the end of the previous accounting period.
Total credit sales from the sales day book (sales journal).
Sales returns (return inwards)
Total sales returns from the return inwards day book (sales returns journal).
From the cash column on the debit side of the cash book.
From the bank column on the debit side of the cash book.
Total of the discount column on the debit side of the cash book.
From the the journal (proper journal).
From the bank column on the debit side of the cash book.
Refunds to trade receivables
From cash/bank column on the credit side of the cash book.
Set off (transfer to purchases ledger)
From the journal (proper journal).
Interest charged on overdue accounts.
From the journal (proper journal).
Closing trade receivables (closing debtors)
Total of trade receivable' balances at the end of the current accounting period.
The following items are often seen in the control account questions. As these times are closely related to the "sales and trade receivables", students often confuse and record them in the S L control account. But these items should not be recorded in the control accounts. Lets check these items below.
Cash sales are recorded cash book but not in the sales ledger. So cash sales should not be entered in the S L control account which checks the arithmetical accuracy of the sales ledger.
If previously written off bad debts are recovered now, it should not be recorded in the S L control account as "bad debts recovered account appears in the general ledger but not in the sales ledger.
3. Increase or decrease in the provision for doubtful debts:
Provision for doubtful debts account is kept in the general ledger. An increase or decrease in the provision for doubtful debts affects the general ledger but not the sales ledger. So it should not be recorded in the S L control accounts.
Trade receivables (debtors) accounts generally shows debit balance in the business books. This balance represents money owed by the trade receivable (debtor) to the business. However some times trade receivable (debtor) account may show a credit balance. It indicates business owes money to the trade receivable. It may happen due to one of the following reasons:

Purchases ledger control account is a summary account which checks the arithmetical accuracy of the purchases ledger. It enables us to see at a glance whether the general ledger balance for the purchases ledger agrees with the total of all the individual trade payable accounts held within the purchases ledger.
This control account typically looks like a "T-account" or a replica of an individual trade payable ( creditor) account, but instead of containing transactions related to one trade payable (creditor) it contains transactions related to all the trade payables (all the creditors) in the business. As this control account contains the summarized information of all the trade payables accounts in the purchases ledger, it is also called as "total trade payables account"("total creditors account").
Check out the format of this control account below and try to perceive the similarities with individual trade payables account (creditors account).
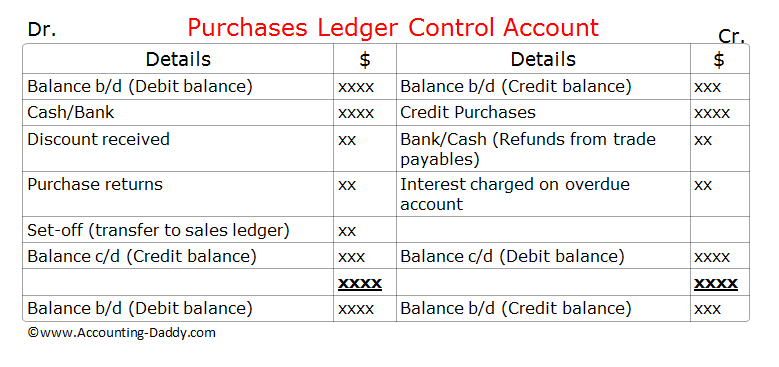
Purchases ledger control account is generally prepared at the end of the financial year or "whenever" it is required to check the arithmetical accuracy of the individual trade payable accounts.
As we discussed earlier, this control account is prepared as an independent check on the arithmetical accuracy of the purchases ledger (creditors ledger). So, we should not obtain the information required to prepare this control account from the purchases ledger (creditors ledger), instead all the information required should be obtained from books of original entry or prime entry.
Once the control account is prepared using the above format with the information obtained from various books of prime entry/original entry, the total of balances on the individual trade paybales accounts (creditors accounts) in the purchases ledger should match with the closing balances on the purchases ledger control account.
If the closing balances of purchases ledger control account and the total of balances on the individual trade payables accounts in the purchases ledger agrees, we can presume that there are no errors in the purchases ledger or fraud occurred in the business. If the balances differ, it indicate that there are errors in the individual trade payables accounts in the purchases ledger or in the control account. So to locate these errors, accountants need to check each and every trade payables account in the purchases ledger carefully until the error is found or the fraud is detected.
The following table provides the details of source of information for the purchases ledger control account items.
Source of information
Opening trade payables (opening creditors)
Total of trade payables balances at the end of the previous accounting period.
Total credit purchases from the purchases day book (purchases journal).
Purchase returns (return outwards)
Total purchase returns from the return outwards day book (purchase returns journal).
From the cash column on the credit side of the cash book.
From the bank column on the credit side of the cash book.
Total of the discount column on the credit side of the cash book.
Refunds from trade payables (creditors)
From cash/bank column on the debit side of the cash book.
Set off (transfer to sales ledger)
From the journal (proper journal).
Interest charged on overdue accounts.
From the journal (proper journal).
Closing trade payables (closing creditors)
Total of trade payables balances at the end of the current accounting period.
The following items are often seen in the control account questions. As these times are closely related to the "purchases and trade payables", students often confuse and record them in the P L control account. But these items should not be recorded in the control accounts. Lets check these items below.
Cash purchases are recorded cash book but not in the purchases ledger. So cash purchases should not be entered in the P L control account which checks the arithmetical accuracy of the purchases ledger.
Trade payables (creditors) accounts generally shows credit balance in the business books. This balance represents money owed to the trade payables (creditors) by the business. However some times trade payable (creditor) account may show a debit balance. It indicates trade payable owes money to the business. It may happen due to one of the following reasons:
Trade receivable is the amount which the company has billed to its customer for selling its goods or supplying the services for which the amount has not been paid yet by the customers and is shown as an asset in the balance sheet of the company.
In simple words, trade receivable is the accounting entry in the balance sheet of an entity, which arises due to the selling of the goods and services on credit. Since an entity has a legal claim over its customer for this amount and the customer is bound to pay the same, it classifies as current asset in the balance sheet of the entity. Trade receivables and accounts receivable are used interchangeably in the industry.
Similar to accounts receivables, company’s also have non-trade receivables, which arises on account of transaction unrelated to the regular course of business.
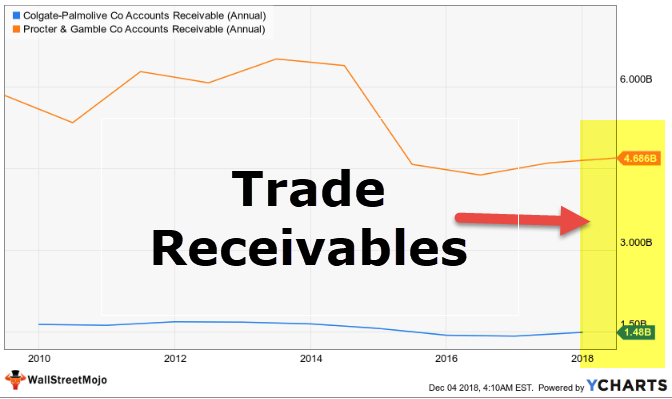
Below is the standard format of the balance sheet of an enterprise.
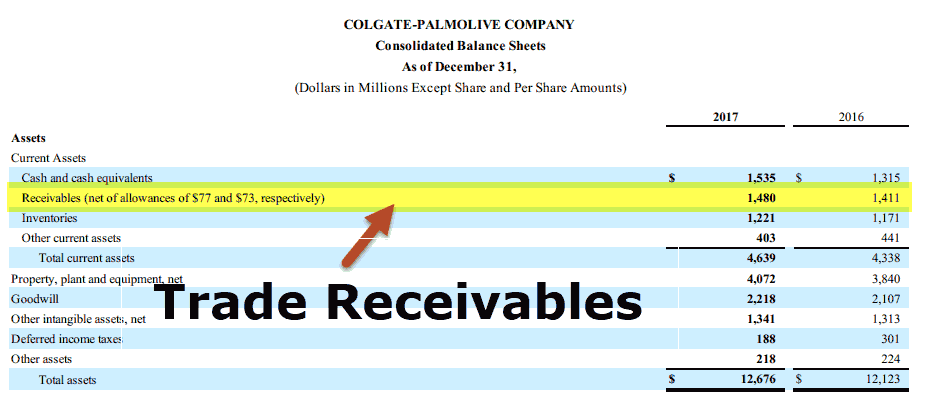
It is generally classified under the current assets in a balance sheet.
ABC corporation is an electrical equipment manufacturing company. It recorded a sales of USD 100 billion in FY18 with 30% sales on credit to its corporate customers. The trade receivables accounting entry for the transaction in its balance sheet will be as below:
Accounts receivables in the above example is calculated below:
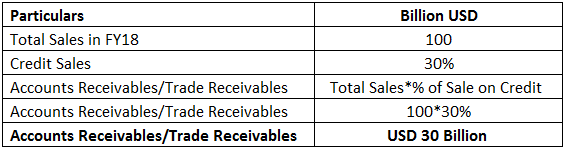
In this example, accounts receivables will be recorded as USD 30 billion in the current asset head in the balance sheet.
I will try to demonstrate why accounts receivables are very critical for the liquidity of companies, and many a time becomes the sole reason for companies becoming bankrupt. The liquidity analysis of an enterprise comprises of a company’s short-term financial positions and its ability to pay its short-term liabilities.
One of the most important metrics we look at while analyzing the liquidity positions of companies is the cash conversion cycle. The cash conversion cycle is the number of days which an enterprise takes to convert its inventory into cash.
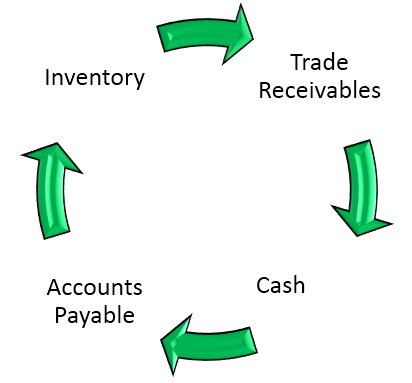
The above picture explains it in more detail. For an enterprise, it starts with the purchase of inventory, which may be on cash or credit purchase. The enterprise converts that inventory into finished goods and makes sales out of it. The sales are made or cash or credit. The sales made on credit is recorded as trade receivables. So the cash conversion cycle is the total number of days it takes for an enterprise to convert its inventory into final sales and realization of cash.
The formula to calculate the cash conversion cycle is as below:
From the above formula, it is evident that a company with a significantly higher proportion of trade receivables will have higher days’ receivables and, therefore, a higher cash conversion cycle.
Note: of course, the cash conversion cycle depends on the other two factors, also which are days inventory outstanding and days payables outstanding. However, here to explain the impact of receivables, we have kept the other two parameters indifferent.
A higher cash conversion cycle for an enterprise may lead to a significantly increased working capital loan requirement to meet its short-term demand for day to day operations. Once such receivables level reaches the alarming degree, it may create serious trouble for the enterprise creating short-term liquidity issues where the company will not be able to fund its short-term liabilities and which may further lead to suspending operations of the company.
A company avails working capital loans to meet its short-term requirements for day to day operations. The assessment for the amount of working capital limit is carried out by lenders taking into account all the current assets of the company. Since receivables make an essential and considerable part of the total current assets of the company, it is critical for lenders to access the level of trade receivables as well as the quality of receivables to approve working capital limits for the company.
The liquidity analysis and interpretation for the level of trade receivables should always be looked into in the context of the specific industry. Certain industries operate in an environment with a high level of receivables. A typical example of the same is electricity generation companies operating in india, where receivables level are very high and days receivable for generation companies varies between as low as one month to as high as nine (9) months.
On the other side, some companies operate with virtually very few or no trade receivables. Companies operating and toll road project developers and operators have very fewer accounts receivables as their revenue is toll collection from commuters on the road. They collect the toll from commuters as and when they pass by toll plaza.
So for a meaningful analysis, one should look at the receivables levels of the top 4-5 companies in the respective industry. If your target company has higher receivables in comparison, than it is doing something wrong either in terms of business model or client/customer targeting or incentives in terms of credit sales to promote sales.
To conclude, one can safely assume that lower the receivables level and days receivables, better the liquidity position for the company.
This has been a guide to trade receivables. Here we discuss its definition, how it works. Examples and see why trade receivables are critical for the liquidity of companies. You can learn more about accounting from the following articles –
Learning objectives:
Understand the procedure of preparing trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet of a business.
Trading point of financial instruments limited is authorised and regulated by the cyprus securities and exchange commission (cysec) (licence number 120/10).
Among the currencies available for trading there are:
any account holder can have his own bonus!
In the forex currency market there are a large number of currency pairs available for trading.
Free spin bonuses are a type of no deposit casino bonuses. These bonuses grant the player the possibility to play a certain number of spins on selected slot machines.